Lameness is one of the biggest challenges facing Irish dairy farmers today. It reduces cow comfort, lowers fertility, cuts milk yield, and eats into farm profitability.
The good news? With the right hoof care routine and consistent footbath management, lameness can be greatly reduced — saving time, money, and stress.
Why Hoof Health Matters
Healthy hooves are the foundation of a productive herd. When cows have strong, pain-free feet, they:
- Walk more willingly to grass
- Stand comfortably in the parlour
- Maintain good feed intakes and milk output
Neglected hooves, on the other hand, lead to problems like white line disease, sole ulcers, and digital dermatitis — issues that are painful for cows and costly for farmers.
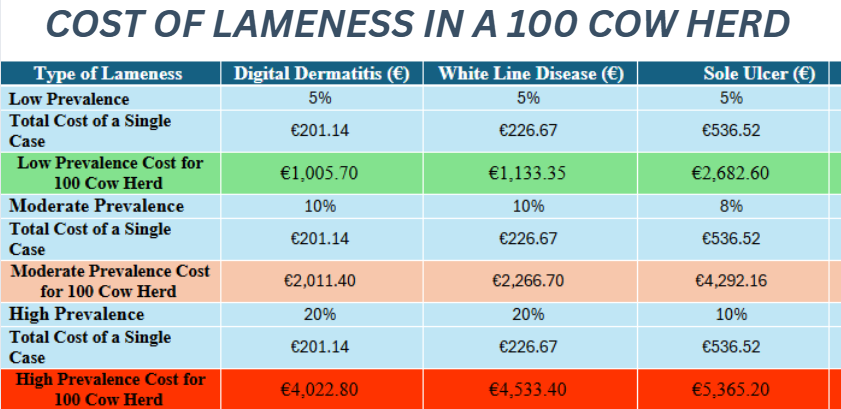
Animal Health Ireland have put together the approximate cost of lameness for a 100 cow
Hoof Trimming: Prevention First
On many farms, trimming only happens when a cow is already lame. By then, the damage is done. Regular preventative hoof trimming keeps feet balanced and avoids uneven wear that can cause bruising, ulcers, and cracks.
Best practice:
- Inspect each cow at least once or twice a year
- Focus on cows walking on concrete or stony roadways (higher risk of overgrowth)
- Use trained hoof trimmers who follow the Dutch Method to restore balance
Spotting Cows That Need Attention:
If time or labour is tight, mobility scoring is a practical way to prioritise cows for inspection. Any cow scoring 2 or 3 should be checked straight away.
Other high-risk cows include:
- Older cows
- Cows with visible hoof overgrowth
- Cows with a history of lameness
- Animals drifting to the back of the herd
Footbaths: Stopping Infections Before They Spread , While trimming prevents mechanical issues, footbathing prevents infectious diseases such as:
- Digital dermatitis (Mortellaro)
- Foul-in-the-foot
- Slurry heel
Remember: footbaths are preventative, not a cure for lame cows.
Frequency guidelines:
High-risk herds: daily footbathing may be needed
Lower-risk herds: once or twice per week
Footbath Setup: Getting It Right
For maximum effectiveness, a footbath should be:
- 3 m long
- 750–850 mm wide
- 100–125 mm deep
- Located at or near the parlour exit
- Narrow enough so cows can’t sidestep
Mixing example:
A bath 3 m × 0.8 m × 0.125 m holds 300 litres of water. To make a 5% solution, add 15 litres of product. Always follow manufacturer and vet guidelines.
Building a Hoof Health Plan
A strong hoof care strategy combines both trimming and footbathing.
Key steps include:
- Routine mobility scoring
- Prompt treatment of lameness cases
- Regular hoof trimming
- Consistent recording of lameness incidents
- Strategic footbath use when infection risk is present
Final Word
Investing in hoof health is investing in herd performance. Fewer lame cows mean:
- Better animal welfare
- Higher milk yields
- Improved fertility
- Lower vet and treatment costs
- Healthy feet mean healthier cows — and healthier cows mean a healthier bottom line.
Hoof Trimming: Prevention First
On many farms, trimming only happens when a cow is already lame. By then, the damage is done. Regular preventative hoof trimming keeps feet balanced and avoids uneven wear that can cause bruising, ulcers, and cracks.
Best practice:
- Inspect each cow at least once or twice a year
- Focus on cows walking on concrete or stony roadways (higher risk of overgrowth)
- Use trained hoof trimmers who follow the Dutch Method to restore balance
Spotting Cows That Need Attention
If time or labour is tight, mobility scoring is a practical way to prioritise cows for inspection. Any cow scoring 2 or 3 should be checked straight away.
Other high-risk cows include:
- Older cows
- Cows with visible hoof overgrowth
- Cows with a history of lameness
- Animals drifting to the back of the herd
Footbaths: Stopping Infections Before They Spread
While trimming prevents mechanical issues, footbathing prevents infectious diseases such as:
- Digital dermatitis (Mortellaro)
- Foul-in-the-foot
- Slurry heel
Remember: footbaths are preventative, not a cure for lame cows.
Frequency guidelines:
- High-risk herds: daily footbathing may be needed
- Lower-risk herds: once or twice per week
Footbath Setup: Getting It Right
For maximum effectiveness, a footbath should be:
- 3 m long
- 750–850 mm wide
- 100–125 mm deep
- Located at or near the parlour exit
- Narrow enough so cows can’t sidestep
Mixing example:
A bath 3 m × 0.8 m × 0.125 m holds 300 litres of water. To make a 5% solution, add 15 litres of product. Always follow manufacturer and vet guidelines.
Building a Hoof Health Plan
A strong hoof care strategy combines both trimming and footbathing. Key steps include:
- Routine mobility scoring
- Prompt treatment of lameness cases
- Regular hoof trimming
- Consistent recording of lameness incidents
- Strategic footbath use when infection risk is present
Final Word
Investing in hoof health is investing in herd performance. Fewer lame cows mean:
- Better animal welfare
- Higher milk yields
- Improved fertility
- Lower vet and treatment costs
Healthy feet mean healthier cows — and healthier cows mean a healthier bottom line.

